{ Box Model. }
Objectives:
By the end of this chapter, you should be able to:
- Explain what the box model is
- Compare and contrast margin, padding and border
- Use properties like
box-sizingto better calculate width and height
The Box Model
Now that we have an idea around basic color and typography, let's see how to add some space around our elements and the content inside. In order to do that, we first have to understand what the box model is. But before we explain the box model, let's make sure we understand some basic properties for adding space between elements and content.
width - The width CSS property specifies the width of the content area of an element.
height - The height CSS property specifies the height of the content area of an element.
margin - used to generate space around elements. margin is a shorthand for margin-top, margin-right, margin-bottom and margin-left.
padding - The padding property in CSS defines the innermost portion of the box model, creating space around an element's content, inside of any defined margins and/or borders. padding is a shorthand for padding-top, padding-right, padding-bottom and padding-left.
border - The border property defines the space between an element's padding and margin. border is shorthand for border-top, border-right, border-bottom and border-left.
div { /* This: */ margin: 20px; /* Is the same as: */ margin-top:20px; margin-right:20px; margin-bottom:20px; margin-left:20px; /* This: */ padding: 10px 20px; /* Is the same as: */ padding-top:10px; padding-right:20px; padding-bottom:10px; padding-left:20px; } h1 { /* This: */ margin: 20px 10px 5px; /* Is the same as: */ margin-top:20px; margin-right:10px; margin-bottom:5px; margin-left:10px; } h2 { /* This: */ margin: 10px 20px; /* Is the same as: */ margin-top: 10px; margin-right: 20px; margin-bottom: 10px; margin-left: 20px; }
Now that we understand this, we can think of every single element on a web page as a rectangular box.
From MDN:
In a document, each element is represented as a rectangular box. Determining the size, properties — like its color, background, borders aspect — and the position of these boxes is the goal of the rendering engine.
In CSS, each of these rectangular boxes is described using the standard box model. This model describes the content of the space taken by an element. Each box has four edges: the margin edge, border edge, padding edge, and content edge.
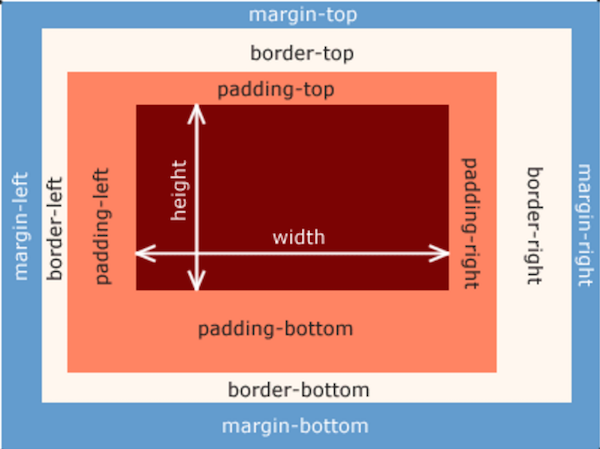
The true width/height of an element is comprised of its width/height + padding + border. Margin is not counted when calculating the true width/height!
div { width: 200px; height: 200px; margin: 20px; padding: 20px; border: 20px solid black; } /* True width = width (200px) + padding-left(20px) + padding-right(20px) + border-left (20px) + border-right (20px) = 280px */ /* True height = width (200px) + padding-top(20px) + padding-bottom(20px) + border-top (20px) + border-bottom (20px) = 280px */
Additional CSS properties
Let's quickly examine two more properties pertaining to the box model: box-sizing and border-radius. First, take a look at this example:
div { box-sizing: border-box; }
By default, the box-sizing property is set to content-box, which means that the width and height property values correspond to the width and height of the content area only. When set to border-box, however, the width and height property values correspond to the width and height of content + border + padding.
Also, in CSS3 we can add rounded corners (and turn our boxes into rounded shapes) using the border-radius property:
div { background-color: blue; border-radius: 10px; }
What happens as you increase/decrease the value of border-radius? Create a simple HTML page to explore this question!
When you're ready, move on to Basics Exercise
